Understanding Food and Beverage Trends 2025
Food and beverage trends are rewriting the rules of what ends up on our plates. Every year, innovations reshape the market, yet artificial intelligence and advanced manufacturing are now transforming how products are made, marketed, and even eaten. It sounds like science fiction but this year sustainability and personalisation are turning from buzzwords to daily realities. The real surprise is just how fast consumers are demanding these changes and how businesses must reinvent themselves or risk being left behind.
Quick summary
Takeaway | Explanation |
|---|---|
Food trends reflect consumer priorities. | Trends show emerging consumer values like health, sustainability, and convenience that businesses must consider. |
Social media accelerates culinary trends. | Platforms like TikTok rapidly spread new food experiences, changing consumer behaviour within weeks. |
Understanding trends drives business innovation. | Businesses can leverage trend insights to create new products and marketing strategies that meet consumer demands. |
Sustainability is a core consumer expectation. | Consumers now prioritise sustainable practices, making this a crucial area for food producers and restaurants. |
Adaptation to trends enhances brand relevance. | Engaging meaningfully with current trends helps build customer trust and strengthens brand loyalty. |
What are food and beverage trends?
Food and beverage trends represent dynamic shifts in consumer preferences, production methods, and culinary experiences that continuously reshape how people select, prepare, and consume food and drink. These trends emerge from a complex interplay of cultural, technological, economic, and social influences, offering insights into evolving consumer behaviours and market dynamics.
Understanding the core drivers
Food and beverage trends are not random occurrences but carefully constructed responses to broader societal changes. Research from food industry experts suggests that emerging trends typically reflect deeper consumer motivations such as:
Health and wellness priorities
Environmental sustainability concerns
Cultural diversity and global culinary exploration
Technological innovations in food production
Economic accessibility and convenience
These multifaceted drivers create a complex ecosystem where consumer preferences continuously evolve, challenging food and beverage producers to remain adaptive and responsive.
Trend characteristics and market impact
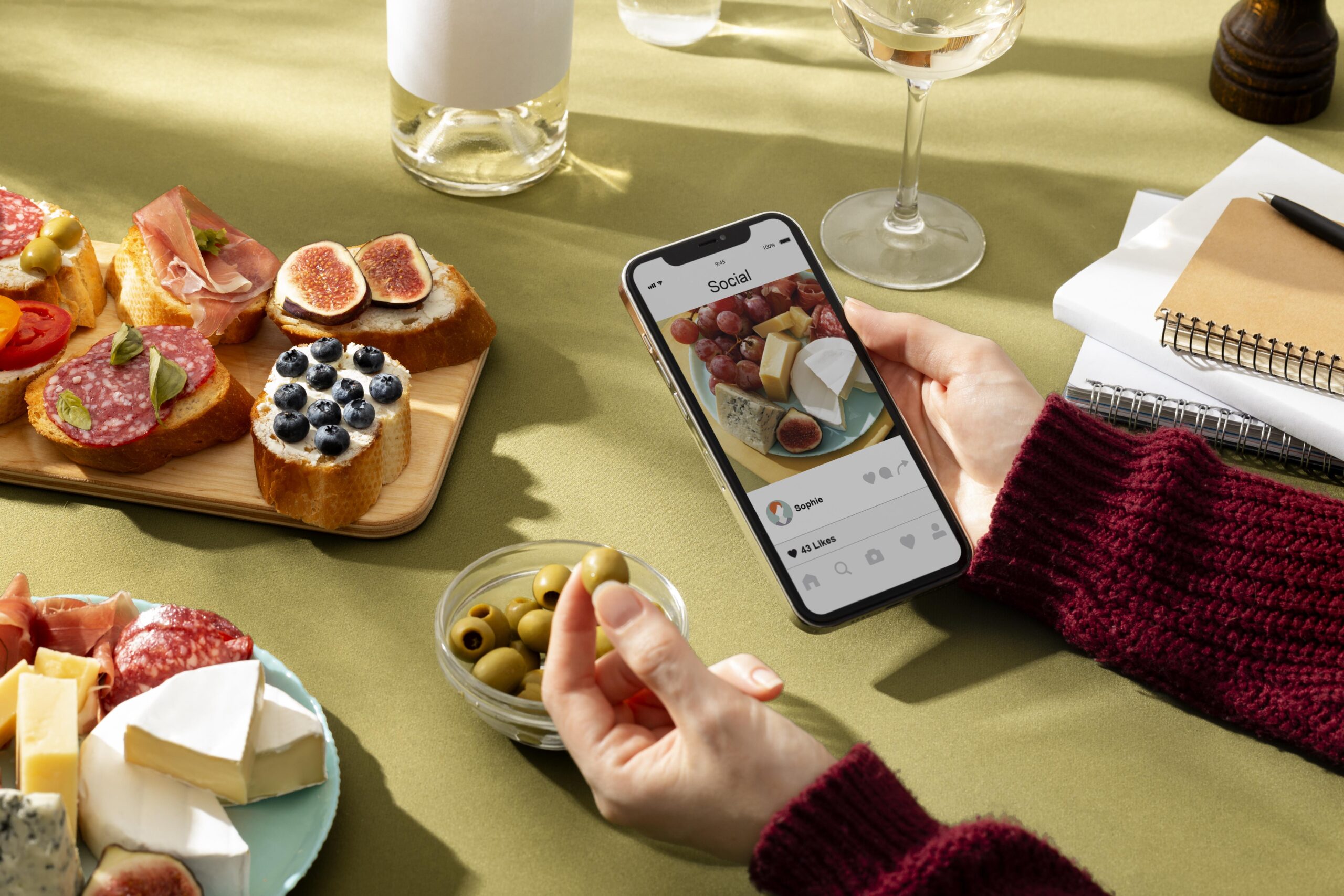
Modern food and beverage trends are distinguished by their rapid emergence and widespread digital amplification. Social media platforms, particularly TikTok food trend channels, have become powerful accelerators of culinary innovations, enabling global audiences to discover and adopt new gastronomic experiences within weeks.
These trends are not merely aesthetic preferences but represent significant economic opportunities. Restaurants, manufacturers, and hospitality businesses must continuously monitor and interpret these shifts to remain competitive. Strategic trend awareness allows businesses to anticipate consumer demands, develop innovative products, and create targeted marketing strategies that resonate with emerging consumer expectations.
Ultimately, food and beverage trends reflect our collective cultural narrative—capturing moments of innovation, reflecting societal values, and providing a delicious lens through which we understand human connection and creativity.
Why food and beverage trends matter for the industry
Food and beverage trends are more than fleeting consumer preferences; they represent critical strategic insights that drive business innovation, competitive positioning, and long-term sustainability across the hospitality and culinary sectors. Understanding these trends enables businesses to navigate complex market dynamics and anticipate emerging consumer demands.
Economic and strategic significance
Research from the International Food Policy Research Institute reveals that tracking food and beverage trends is essential for businesses seeking to remain relevant and profitable. These trends provide crucial intelligence about market transformations, helping companies develop targeted strategies that align with consumer expectations.
Key strategic implications include:
Predicting consumer behaviour shifts
Identifying potential market opportunities
Developing innovative product offerings
Understanding competitive landscape changes
Mitigating investment risks
Innovation and competitive advantage
Trends serve as powerful catalysts for innovation within the food and beverage industry. Businesses that proactively interpret and respond to emerging trends can differentiate themselves, creating unique value propositions that attract and retain customers. Explore our comprehensive guide on restaurant trends to understand how strategic trend adoption can transform business models.
For instance, the rising demand for sustainable and plant-based products has prompted numerous restaurants and food manufacturers to redesign their menus and product lines, demonstrating how trend awareness can drive significant operational and strategic shifts.
Consumer connection and brand relevance
Food and beverage trends represent more than economic opportunities; they are powerful communication tools that help businesses connect with their target audiences. By demonstrating an understanding of evolving consumer preferences, companies can build trust, enhance brand perception, and create more meaningful customer relationships.
Ultimately, embracing food and beverage trends is not about chasing temporary fads, but about developing a nuanced, responsive approach to understanding and serving consumer needs in an increasingly dynamic marketplace.

How consumer behaviour influences food and beverage trends
Consumer behaviour serves as the fundamental driving force behind food and beverage trends, acting as a complex ecosystem where individual preferences, societal values, and market dynamics continuously interact and evolve. Understanding these intricate relationships provides critical insights into how consumer choices shape industry innovations and market transformations.
Psychological and social drivers
Research from Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis reveals that consumer food choices are motivated by multifaceted psychological and social factors beyond simple nutritional requirements. Consumers increasingly view their dietary selections as expressions of personal identity, ethical commitments, and lifestyle philosophies.
Economic and practical considerations
Economic constraints and practical considerations play a significant role in shaping consumer food preferences. Purchasing decisions are heavily influenced by factors such as affordability, convenience, and perceived value. Check out our seasonal food trend guide to understand how economic factors drive culinary innovations. For example, rising living costs have prompted consumers to seek more cost-effective dining options, leading to increased interest in affordable, high-quality meal alternatives that balance nutrition and budget constraints
Technology and information access
Digital platforms and unprecedented access to information have dramatically transformed consumer food choices. Social media, online reviews, and global connectivity enable consumers to discover, share, and adopt culinary trends with unprecedented speed and reach. This technological empowerment means consumers are more informed, critical, and adventurous in their food selections. They actively seek experiences that align with their personal values, whether through sustainable practices, cultural authenticity, or innovative culinary techniques.Ultimately, consumer behaviour represents a powerful, dynamic force that continuously reshapes the food and beverage landscape, challenging businesses to remain agile, responsive, and deeply attuned to evolving societal preferences. This table outlines the primary psychological, economic, and technological drivers influencing contemporary consumer behaviour in the food and beverage sector.

Driver Type |
Key Factors & Motivations |
|---|---|
Psychological/Social |
Health goals, personal identity, social media, ethical concerns. |
Economic |
Affordability, convenience, value. |
Technological |
Access to information, social sharing, global connectivity |
Sustainability and ethical consumption
Sustainability has evolved from a niche preference to a fundamental consumer expectation, driving significant innovations across the food and beverage sector. Experts in food industry research indicate that ethical consumption now represents a holistic approach encompassing environmental, social, and economic considerations.
Key sustainability principles include:
Carbon footprint reduction in food production
Regenerative agricultural practices
Transparent supply chain management
Circular economy food systems
Ethical labour and fair trade practices
Holistic wellness and functional nutrition
The concept of food as medicine has gained significant momentum, with consumers seeking nutritional experiences that deliver comprehensive wellness benefits. This shift represents a profound understanding that diet is not merely about sustenance but about proactive health management. Modern consumers are increasingly interested in functional foods and beverages that offer targeted health benefits, such as immune system support, cognitive enhancement, stress reduction, and metabolic optimisation. This trend reflects a growing recognition of the intricate connections between diet, mental health, and overall physiological well-being. These key concepts demonstrate that food and beverage trends in 2025 are not just about taste and convenience, but about creating meaningful, responsible, and personalised nutritional experiences that align with broader societal values and individual aspirations. The following table compares the three key concepts shaping food and beverage trends in 2025, summarising their core focus and main influences.
Real-world examples of emerging food and Beverage trends
The theoretical concepts of food and beverage trends manifest dramatically through tangible, innovative practices transforming culinary landscapes worldwide. These real-world examples demonstrate how emerging trends translate from abstract ideas into practical, consumer-facing experiences that reshape our understanding of nutrition, sustainability, and gastronomic pleasure.
Sustainable culinary practices
Sustainability has transformed from a conceptual ideal to a practical approach in food production and consumption. Explore modern cooking techniques that demonstrate how chefs and food producers are reimagining traditional practices through an environmentally conscious lens. Restaurants and food producers are implementing zero-waste cooking strategies, utilising entire ingredients, developing closed-loop production systems, and creating innovative recycling mechanisms that minimise environmental impact while maintaining exceptional culinary standards.

Technological integration in food experience
Technology is revolutionising how consumers interact with food, creating personalised, immersive experiences that go beyond traditional dining. Advanced technologies enable hyper-customised nutrition, interactive dining experiences, and unprecedented transparency in food sourcing. Examples include augmented reality menus that provide detailed ingredient traceability, AI-powered nutrition recommendations tailored to individual genetic profiles, and blockchain technologies ensuring complete supply chain transparency. These technological interventions represent a profound shift from passive consumption to active, informed engagement with food systems.
Frequently asked questions
The key drivers include health and wellness priorities, environmental sustainability concerns, cultural diversity, technological innovations in food production, and economic accessibility.
Technological advancements enable hyper-personalised nutrition, customised meal plans, and innovative production techniques, allowing for greater culinary creativity and consumer engagement.
Sustainability has become a fundamental consumer expectation, promoting ethical consumption practices that focus on reducing carbon footprints, improving transparency in supply chains, and fostering environmentally friendly production methods.
Examples include mushroom-based meat alternatives, probiotic-infused beverages, adaptogenic herbs, and cellular agriculture protein sources, showcasing the integration of functional ingredients into everyday diets.
Ready to take bookings seriously?
Try Tableo’s free version for up to 100 covers monthly– no credit card, no fuss.
Free Version – Free Setup – Free Training – Free Support


Stephanie Paris
Gen-Z marketing coordinator bringing fresh energy to web and graphic design, with a weekend habit of chasing adventure.